Anti-inflammatory Strawberries and Honey : Relationship Between Inflammatory and Oxidative Stress
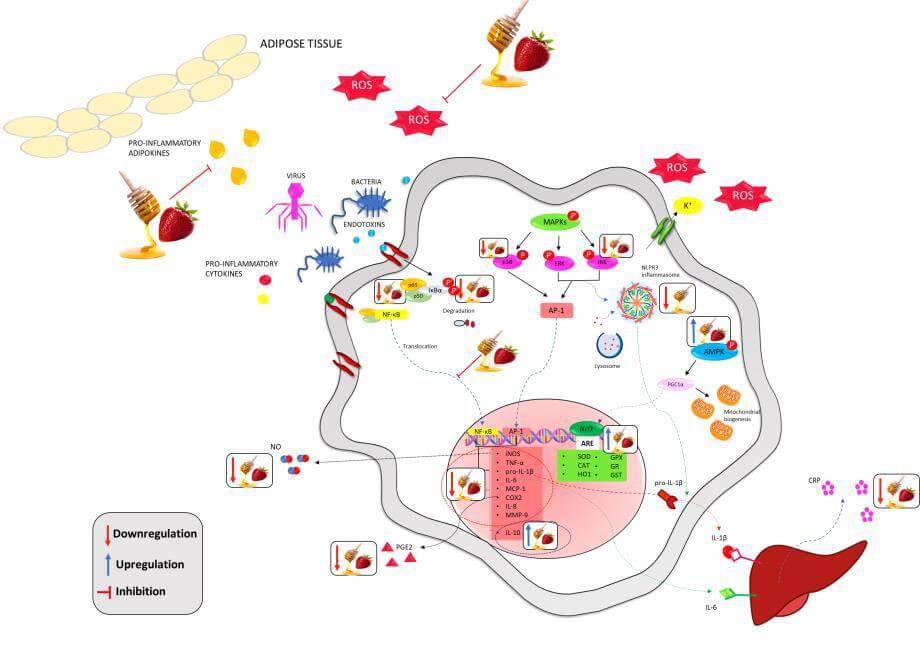
Fig. 1. The relationship between inflammatory and oxidative stress. Activation of macrophages and
mitochondrial respiration increase ROS production that leads to tissue oxidation and activates
cellular signaling pathways MAPKs, PK13, NF-κB and NLRP3 inflammasome. NF-κB upregulates
proinflammatory cytokines, COX-2, NOS. TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1 stimulate in turn macrophages and
neutrophils for inflammation process. NADPH oxidase and uncoupled NOS are also responsible for
ROS production that causes tissue oxidation, necrosis and DNA damage. Necrosis of tissue
activates, via TRL4 receptor, HMGB1 that in turn activates NF-κB and NLRP3 inflammasome.
Nrf2 play a significant role for NLRP3 activation by upregulating HO-1 and reducing oxidative
stress by inhibiting NF-κB signaling and vice versa.
Fig. 1. The relationship between inflammatory and oxidative stress. Activation of macrophages and
mitochondrial respiration increase ROS production that leads to tissue oxidation and activates
cellular signaling pathways MAPKs, PK13, NF-κB and NLRP3 inflammasome. NF-κB upregulates
proinflammatory cytokines, COX-2, NOS. TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1 stimulate in turn macrophages and
neutrophils for inflammation process. NADPH oxidase and uncoupled NOS are also responsible for
ROS production that causes tissue oxidation, necrosis and DNA damage. Necrosis of tissue
activates, via TRL4 receptor, HMGB1 that in turn activates NF-κB and NLRP3 inflammasome.
Nrf2 play a significant role for NLRP3 activation by upregulating HO-1 and reducing oxidative
stress by inhibiting NF-κB signaling and vice versa.
See featured image at https://foodary.com/1479/anti-inflammatory-strawberries-and-honey/ for details
